Regression models are formally introduced in Algebra 1; however, the standards for require that students analyze further to compute, with technology, and interpret the correlation coefficient of a linear fit (HSS-ID.C.8) and informally assess the fit of a function by plotting and analyzing residuals (HSS-ID.B.6b).
Students can use residuals, specifically a residual plot, to assess the appropriateness of the selected regression model. The difference between the observed function value (data) and the predicted function value (regression equation) is a residual. Each data point has one residual. A residual plot is a graph that shows the residuals on the vertical axis with respect to the independent variable on the x-axis.
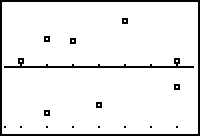 |
| Residual Plot |
The correlation coefficient (and the coefficient of determination) will be computed on the TI-84 graphing calculator when a regression equation is calculated.
 |
| Note: If you only see the regression equation details, go to MODE and select ON for Stat Diagnostics. |
These TI-84 calculator hints support Common Core State Standards HSS-ID.B.6b and HSS-ID.C.8 included in 7th and 8th Accelerated Algebra 1.






+Title+Pic.png)
.jpg)
